Sexual Dysfunctions , Paraphilic Disorders and Gender Dysphoria
Sexual disorders encompass a wide range of issues that cause clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning. Understanding the nuances of sexual disorders and their presentations is crucial for psychiatrists preparing for the ABPN Psychiatry exam. It’s vital to approach these disorders with sensitivity and awareness of cultural influences, as well as being adept at differentiating sexual disorders from other psychiatric conditions. This chapter will explore key concepts related to various sexual disorders, from dysfunctions to paraphilic disorders and gender dysphoria.
Sexual dysfunctions
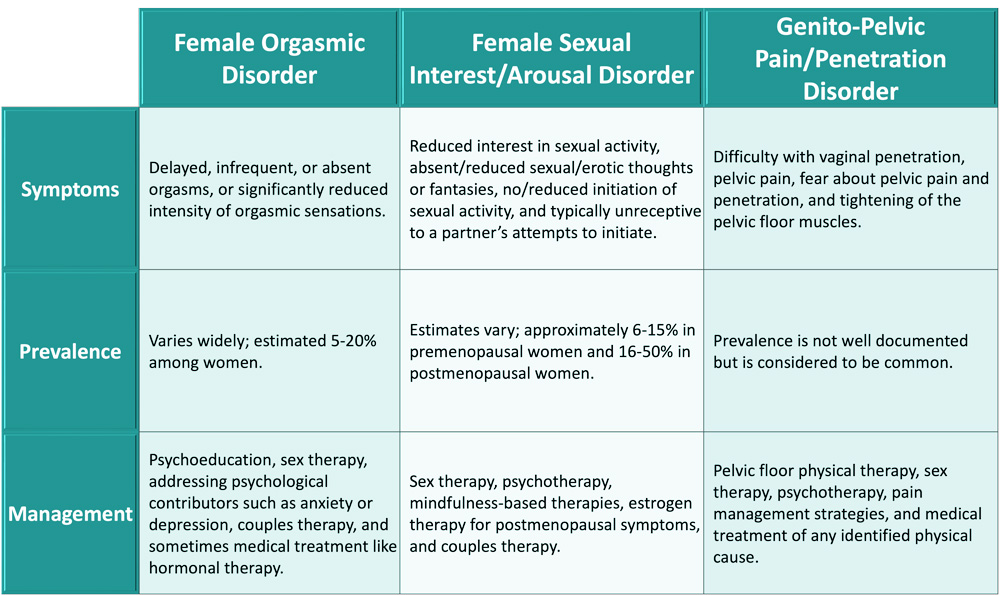
Female orgasmic disorder
- Persistent difficulty or inability to reach orgasm during sexual activity.
- Risk Factors include history of pelvic surgery or sexual abuse, cultural or religious restrictions, and interpersonal issues.
- Treatment:
- Psychotherapy
- Relationship counseling
- Addressing underlying medical conditions or medication side effects
Female sexual interest/arousal disorder
- Persistent lack of, or significantly reduced, sexual interest or arousal
- Associated with reduced testosterone levels
- Etiologies:
- Menopause
- Pregnancy
- Breastfeeding
- Contraceptive use
- Psychiatric disorders (e.g., depression, anxiety).
- Treatment:
- Address underlying issues
- Hormone therapy
- Psychotherapy
- Relationship counseling
- Flibanserin is an FDA-approved medication for the treatment of female sexual interest/arousal disorder in premenopausal women.
- Side effects: Nausea, fatigue, dizziness.
Genito-pelvic pain/penetration disorder
- Involves involuntary contraction of pelvic floor muscles during vaginal entry, pain during deep penetration, anxiety about penetration attempts, or difficulty having intercourse.
- Etiologies:
- Vaginismus
- Vulvodynia
- Endometriosis
- Urinary tract infections
- History of sexual abuse.
- Primary provoked vestibulodynia (PVD): Symptoms of GPPD present at the first experience with penetration.
- Treatment:
- Pelvic floor physical therapy
- Psychotherapy
- Relaxation techniques
- Address underlying medical conditions
- Tricyclic antidepressants (nortriptyline, amitriptyline) can also be used.
Log in to view the remaining 60-90% of page content!
New here? Choose an account!
1 Month Plan
Full Access Subscription
$68
$
48
49
1 Month -
Access to all chapters
-
Access to all images and cases
-
Access to all flashcards
-
Access to Full Question Bank
3 Month Plan
Full Access Subscription
$159
$
73
49
3 Months -
Access to all chapters
-
Access to all images and cases
-
Access to all flashcards
-
Access to Full Question Bank
1 Year Plan
Full Access Subscription
$446
$
195
49
1 Year -
Access to all chapters
-
Access to all images and cases
-
Access to all flashcards
-
Access to Full Question Bank
Popular
Loading table of contents...
Loading table of contents...