Psychotherapy & Somatic Treatments
Psychotherapy is a meticulously structured therapeutic interaction aimed at addressing the psychological, emotional, and behavioral disturbances that manifest in individuals confronting various psychiatric disorders. It serves as a pivotal cornerstone to address the multifaceted landscape of mental health, such as maladaptive thought patterns and affective dysregulation. It is a deliberate and carefully cultivated therapeutic relationship that culminates with behavioral and/or symptomatic therapeutic change, built upon the principles of mutual respect, trust, and active patient engagement.
In this chapter, we explore the theoretical foundations, clinical modalities, and pragmatic applications of various forms of evidence-based psychotherapy. Additionally, the second half of this chapter will address another form of non-pharmacological therapy termed somatic treatments. This encompasses treatments like electroconvulsive therapy, phototherapy, and transcranial magnetic stimulation. Upon reviewing this chapter, you will be better equipped with the psychotherapy tools and somatic treatments essential to navigate the intricate terrain of mental health disorders and ace your ABPN Psychiatry Board examination!
Authors: Anca Toma MD, Brian Hanrahan MDPsychotherapy
Supportive Psychotherapy
- Patient-centric therapy that emphasizes the therapeutic alliance with the patient by offering empathetic understanding and emotional support.
- Effective in mitigating distressing symptoms.
- Used as a short-term treatment strategy, integrating it into a broader treatment plan that may include pharmacotherapy or other therapeutic modalities.
- Utilized in the treatment of acute psychological distress, bereavement, adjustment disorders, and situations where augmenting emotional resilience and adaptive coping mechanisms are paramount.
Cognitive and/or behavioral Therapy (CBT)
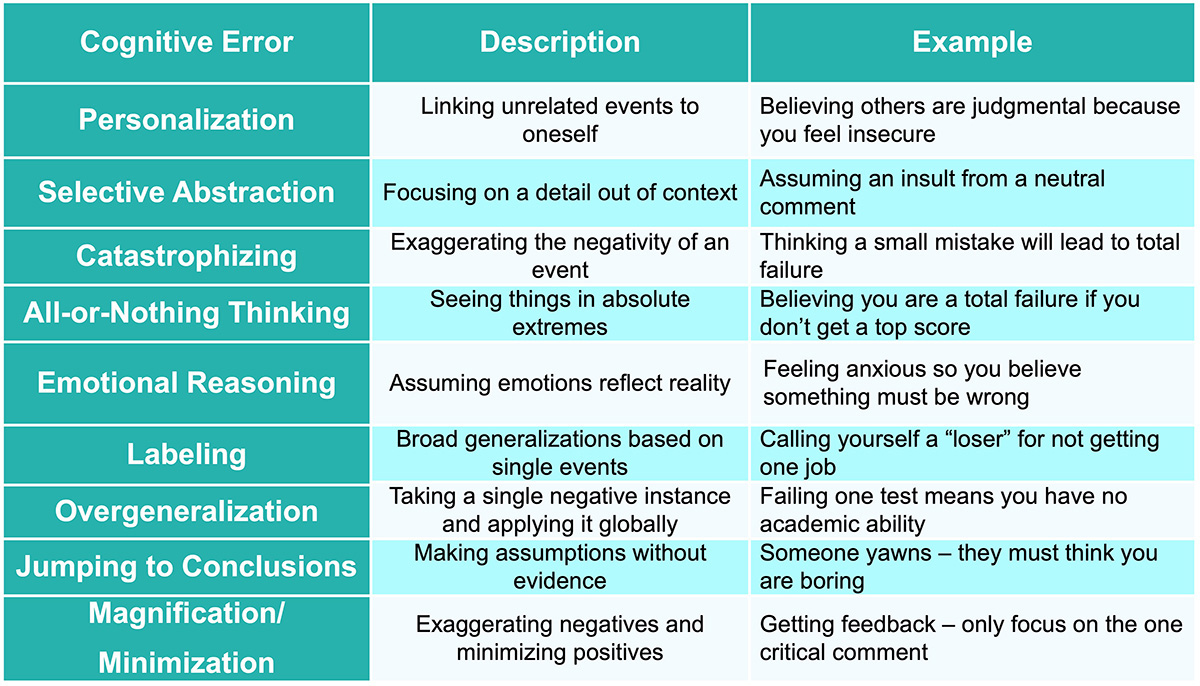
- Focuses on identifying, dissecting, and reformulating maladaptive cognitive schemas, core beliefs, and thought processes that underpin emotional distress and psychopathology.
- Schema: A pattern of thinking and behavior that helps a person make sense of the world (i.e. “I always have to work harder than everyone else to succeed”).
- Core Belief: A strongly rigid, inflexible belief that is maintained by focusing on data that reinforces that belief, and ignoring data that contradicts it (i.e. “I am worthless” ).
- Socratic questioning is the most commonly used CBT technique to uncover and modify automatic negative thoughts. (i.e. Therapist: “You seem to believe that if you ask your boss for time off, he will be angry and fire you. What evidence do you have to support that belief?”)
- The goal of CBT is to modify dysfunctional behaviors that either stem from or trigger cognitive errors.
Log in to view the remaining 60-90% of page content!
New here? Choose an account!
1 Month Plan
Full Access Subscription-
Access to all chapters
-
Access to all images and cases
-
Access to all flashcards
-
Access to Full Question Bank
3 Month Plan
Full Access Subscription-
Access to all chapters
-
Access to all images and cases
-
Access to all flashcards
-
Access to Full Question Bank
1 Year Plan
Full Access Subscription-
Access to all chapters
-
Access to all images and cases
-
Access to all flashcards
-
Access to Full Question Bank